GROUPBY Function in Excel
The GROUPBY function in Excel creates a summary of data via a formula. The GROUPBY function in Excel is a part of lookup and reference formulas.
The GROUPBY function organizes data by grouping rows based on given fields, applying aggregations (like SUM, AVERAGE, or COUNT), and sorting or filtering the results.
How to use GROUPBY Function in Excel
The article in this webpage describes how to use the GROUPBY function in Microsoft Excel with the syntax, arguments, detailed explanation, and examples step by step.
GROUPBY Syntax
=GROUPBY(row_fields, values, function, [field_headers], [total_depth], [sort_order], [filter_array], [field_relationship])
The arguments of GROUPBY function are:
- row_fields (required) – The range containing the values for grouping.
- values (required) – The range containing the values to aggregate.
- function (required) – The function used to do the aggregations.
- field_headers (optional) – A number between 0 and 3 that specifies whether the field data has headers and whether field headers should be returned in the results.
- Automatic (default): Excel to decide based on data.
- 0: No headers.
- 1: Yes – headers in data, but don’t show them.
- 2: No headers in data, but Excel generates them.
- 3: Yes – headers in data and show them.
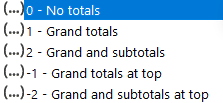
- total_depth (optional) – to show the totals and subtotals at the bottom or top.
- 0: No Totals.
- 1 (default): Grand Totals at the bottom.
- 2: Grand and Subtotals at the bottom.
- -1: Grand Totals at the top.
- -1: Grand and Subtotals at the top.
- sort_order (optional) – A numeric value specifying the sort order for rows in Excel. Use positive numbers for ascending order sorting (default) and negative numbers for descending order sorting.
- filter_array (optional) – Logical expression to filter specific rows.
- field_relationship (optional) – Defines the relationship when multiple columns are in row_fields.
- 0: Hierarchy (default).
- 1: Table.
GROUPBY Examples
Let’s understand the CODE function in Excel with examples.
1. Summary of Data
The GROUPBY function in Excel organizes rows in a specified array by grouping them based on the unique values and calculates a summary for each group.
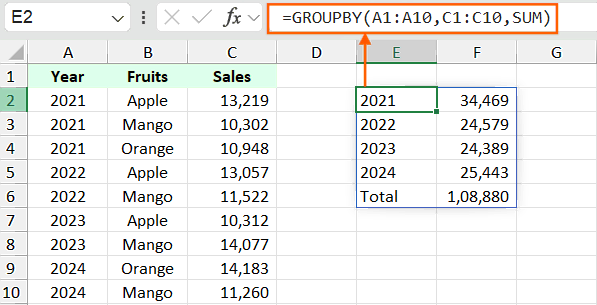
Let’s understand the Excel GROUPBY function with an example. Suppose you have a table of data as shown in the below image and you want the summary of sales based on the year, then the GROUPBY function in Excel will be:
=GROUPBY(A1:A10,C1:C10,SUM)
In this example, the row_fields is A1:A10 containing the years which you want to group, values in C1:C10 and the SUM function to total the values.
Apart from SUM, you can also use the other functions, such as PERCENTOF, AVERAGE, MEDIAN, COUNT, COUNTA, MAX, PRODUCT, ARRAYTOTEXT, CONCAT, STDEV.S, STDEV.P, VAR.S, VAR.P, MODE.SNGL, and LAMBDA.
2. Show Headers
By default, the GROUPBY function does not show the headers. To show the headers in the output, you need to use the argument field_headers in the GROUPBY function.
In the previous example the header was not visible. To show the header select the option 3 for the next argument fileld_headers and the GROUPBY formula will be:
=GROUPBY(A1:A10,C1:C10,SUM,3)
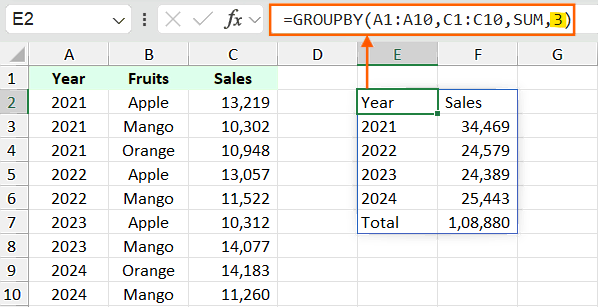
The above GROUPBY function will show headers only if your data contains the header.
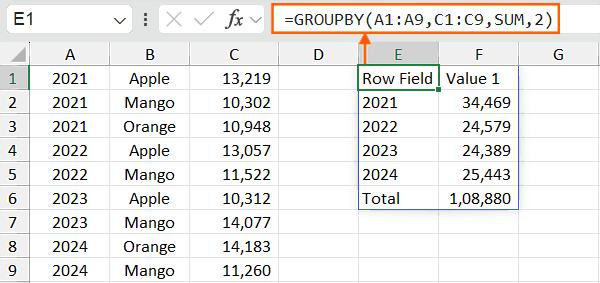
If the data is without headers then use the option 2, so that the Excel will auto generate the headers based on the data and the GROUPBY function will be:
=GROUPBY(A1:A9,C1:C9,SUM,2)
3. Show/Hide Totals
By default, the GROUPBY function shows the total at the bottom. The total_depth argument in GROUPBY function can be used to show or hide the totals and subtotals at the top or bottom.
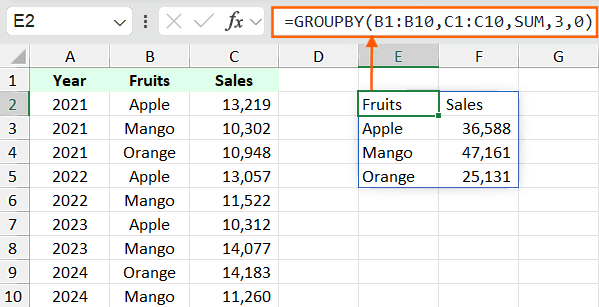
For example, you do not want to show the totals then the GROUPBY function will be:
=GROUPBY(B1:B10,C1:C10,SUM,3,0)
Important Notes
- The GROUPBY function, introduced in Excel 365 as part of dynamic array functions.
- The GROUPBY function is used to group data based on certain criteria and perform operations on the grouped data.
- The GROUPBY function returns #SPILL! error if any adjacent cells contain content, such as text, spaces, or hidden characters, as this prevents the formula from expanding its output into the blocked range.
- The GROUPBY function returns #VALUE! error if the ranges provided in between two arguments have mismatched.
- The GROUPBY function allows for aggregation and summarization of data in a more flexible and powerful way compared to the PivotTable.
Learn More

Excel Formulas (Category)
» Financial Formulas in Excel
» Logical Formulas in Excel
» Text Formulas in Excel
» Date and Time Formulas in Excel
» Lookup and Reference Formulas in Excel
» Math and Trig Formulas in Excel
» Statistical Formulas in Excel
» Engineering Formulas in Excel
» Cube Formulas in Excel
» Information Formulas in Excel
» Compatibility Formulas in Excel
» Web Formulas in Excel
Excel Tutorial Part 1 (Basic)
» Excel Basics
» Excel Home
» Excel Workbook
» Excel Template
» Excel Cell
» Excel Password
Excel Tutorial Part 2 (Format)
» Excel Clipboard
» Excel Format Font
» Excel Format Alignment
» Excel Format Number
» Excel Border
» Excel Conditional Formatting
Excel Tutorial Part 3 (Data)
» Excel Sort Data
» Excel Filter Data
» Excel Text to Columns
» Excel Data Validation
» Excel Flash Fill
» Excel Remove Duplicates
» Excel Relationships
» Excel Consolidate
» Excel What-If Analysis
» Excel Group
» Excel Charts
» Excel Table
» Excel PivotTable
Excel Tutorial Part 4 (Find)
» Excel Find and Replace
» Excel Go To
» Excel Select Objects
» Excel Selection Pane
Excel Tutorial Part 5 (Review)
» Excel Spell Check
» Excel Smart Lookup
» Excel Translate
» Excel Comments & Notes
» Excel Protect
» Excel Hide Ink
Excel Tutorial Part 6 (View)
» Excel Workbook Views
» Excel Formula Bar
» Excel Zoom
» Excel Window
» Excel Macros
Excel Tutorial Part 7 (Fx)
» Excel Formulas (Category)
» Excel Formulas (Alphabetical Order)
» Excel Errors
» Excel Name Manager
» Excel Formula Auditing
» Excel Watch Window
» Excel Calculation Options
Excel Tutorial Part 8 (Other)
» Excel Add-ins
» Excel Shortcuts

0 Comments